Conversion from Open CASCADE to PRT is not supported yet :(
Learn more
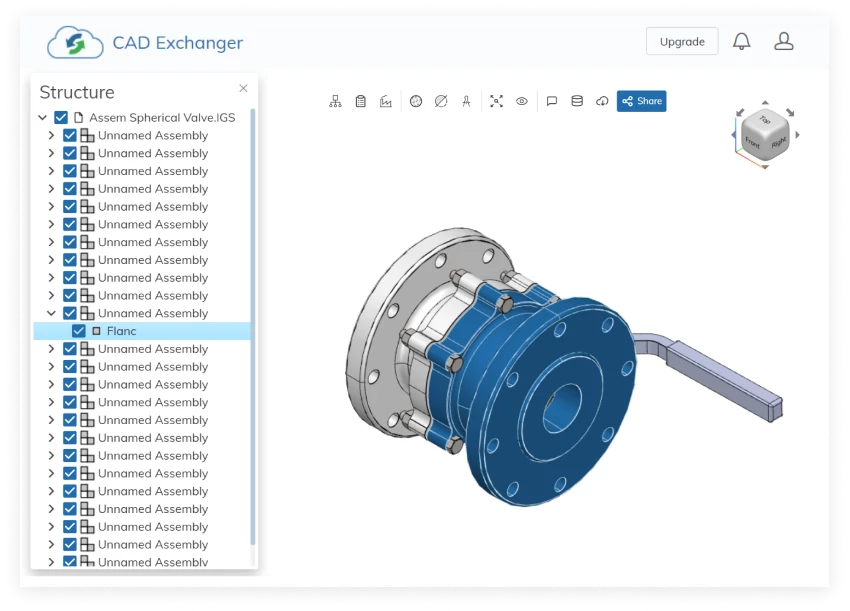
Open CASCADE
In solid modeling and computer-aided design, boundary representation—often abbreviated as B-rep or BREP—is a method for representing shapes using the limits. A solid is represented as a collection of connected surface elements, the boundary between solid and non-solid.
Boundary representation of models are composed of two parts: topology and geometry (surfaces, curves and points). The main topological items are: faces, edges and vertices. A face is a bounded portion of a surface; an edge is a bounded piece of a curve and a vertex lies at a point. Other elements are the shell (a set of connected faces), the loop (a circuit of edges bounding a face) and loop-edge links (also known as winged edge links or half-edges) which are used to create the edge circuits. The edges are like the edges of a table, bounding a surface portion.
Compared to the constructive solid geometry (CSG) representation, which uses only primitive objects and Boolean operations to combine them, boundary representation is more flexible and has a much richer operation set. In addition to the Boolean operations, B-rep has extrusion (or sweeping), chamfer, blending, drafting, shelling, tweaking and other operations which make use of these.
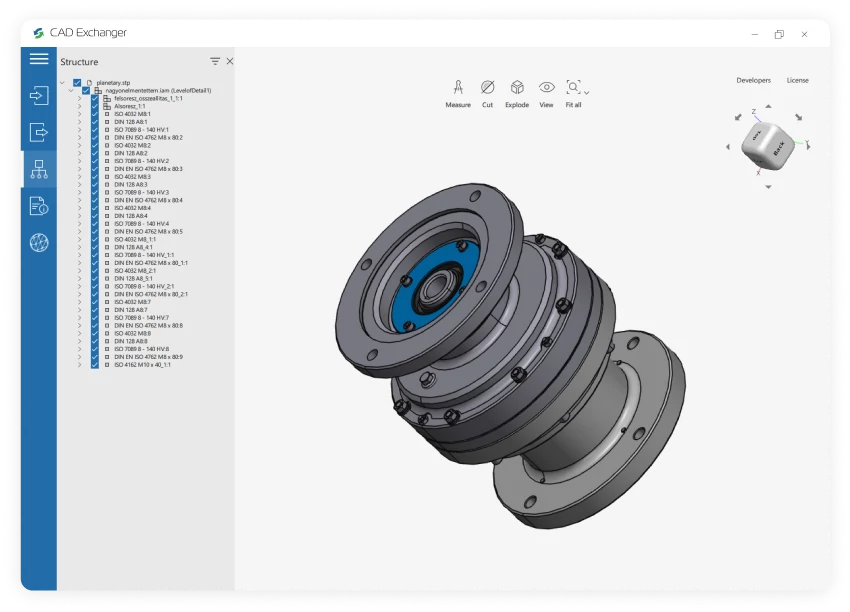
PRT
A PRT format is used to store components of 3D CAD models. It may contain lines, surfaces, textures, dimensions, and metadata.
The .prt extension is mostly associated with the Siemens NX Part (PRT) file type as an acronym for "part". PRT files may be exported to various standard CAD and 3D modeling formats (e.g. OBJ and STL) in addition to being utilized natively in Siemens NX.
The PRT file is also a part created by PTC Creo Parametric 3D software. In PTC Creo, project part files can be combined in a single assembly file with an ASM extension.
Despite the same extension name different CAD software produce PRT files differently, i.e. PRT files produced with Creo are not the same as PRT files generated from NX.
The PRT extension is also compatible with Dassault Systèmes SOLIDWORKS.
From Our Blog
Everything you need to know about CAD file formats
A CAD file is an output of a CAD software, containing key information about the designed object: its geometry and topology representation, 3D model hierarchy, metadata, and visual attributes depending on the format of the file.
Read more
Integration with UNIGINE engine
This article explores the integration possibilities with the UNIGINE engine, a powerhouse in the realm of virtual simulation and game development. Learn how it can be used in applications built with the UNIGINE engine to import CAD and 3D models.
Read more
Manufacturing Toolkit and Web Toolkit enhancements, Unity performance optimization, renaming and rotating SDK examples in release 3.24.0
Explore the wall thickness at a specific point on a surface, enjoy four times faster Unity objects performance, and check out renaming and rotating examples in SDK.
Read more