Conversion from SpaceClaim to IAM is not supported yet :(
Learn more

SpaceClaim is a solid modeling CAD application that runs on Microsoft Windows. It is developed by SpaceClaim Corporation, but now owned by ANSYS.
SpaceClaim’s 3D direct modeling technology is expressed by the following tools: pull, move, fill, and combine.
Pull contains most creation features which can be found in traditional CAD systems. For instance, using the Pull tool on a face by default offsets the face, but using the Pull tool on an edge rounds it.
Move relocates components and geometry, and can also be used to create patterns (often called arrays).
Fill primarily removes geometry from a part by extending geometry to fill in the surrounding area. It is commonly used for deleting rounds and holes from a model.
Combine merges parts and subtracts parts from each other.
IAM
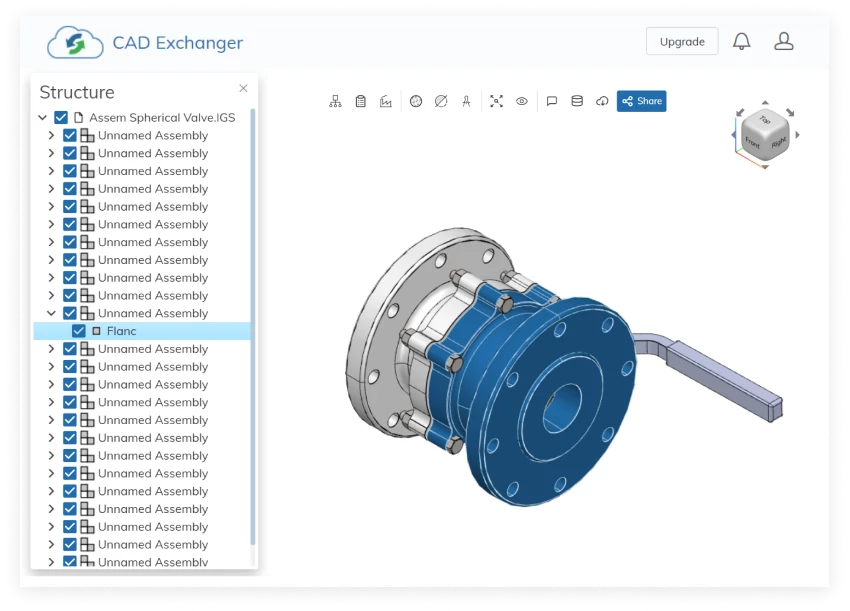
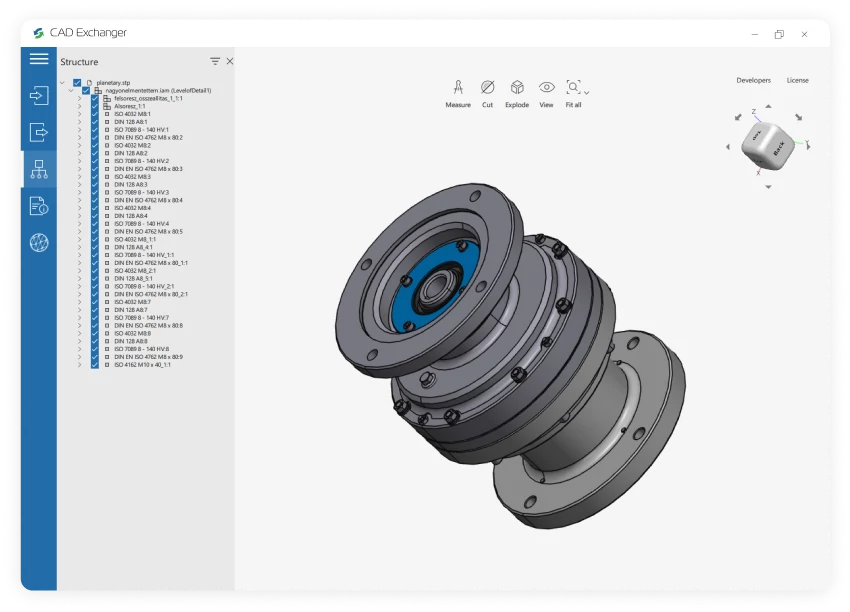
An IAM file is an assembly model created with Inventor CAD and engineering software by Autodesk.
The IAM format comprises parts and subassemblies linked through assembly relationships. A subassembly in an IAM file is a self-contained unit with its collection of parts.
The .iam extension of an Autodesk Inventor Assembly Data File can be viewed using the following software: Autodesk Inventor / Inventor View, and Spaceclaim Engineer software. Autodesk Viewer web application and Fusion 360 integrated CAD / CAM / CAE software environment can import and render an assembly model created with Inventor.
From Our Blog
Everything you need to know about CAD file formats
A CAD file is an output of a CAD software, containing key information about the designed object: its geometry and topology representation, 3D model hierarchy, metadata, and visual attributes depending on the format of the file.
Read more
3D formats overview: Autodesk Inventor
This article dives deep into the details of Autodesk Inventor file format, providing an understanding of its native .ipt and .iam file extensions, as well as its powerful B-Rep representations and assembly structures.
Read more
Docker images, support of Autodesk Inventor 2022, and import of properties from CATIA in CAD Exchanger 3.22.0
Ship your software anywhere with Docker images, read .ipt, .iam files independently from Autodesk software, explore mechanical, product, and custom properties from CATIA.
Read more